Embedded Vision : A Comprehensive Guide | Sinoseen
Embedded vision refers to the integration of computer vision capabilities in embedded devices and systems. In this paper, we will introduce the basic concepts of embedded vision systems and then delve into their various advantages and applications.
What is Embedded Vision?
Embedded vision refers to a machine that understands its surroundings through visual methods, and simply refers to the use of computer vision techniques in embedded systems, which involves two technologies: embedded systems and computer vision (sometimes referred to as machine vision). In other words, “embedded vision” refers to an embedded system that extracts meaning from visual input. Embedded systems can be any microprocessor-based system that does a specific job and is available everywhere.
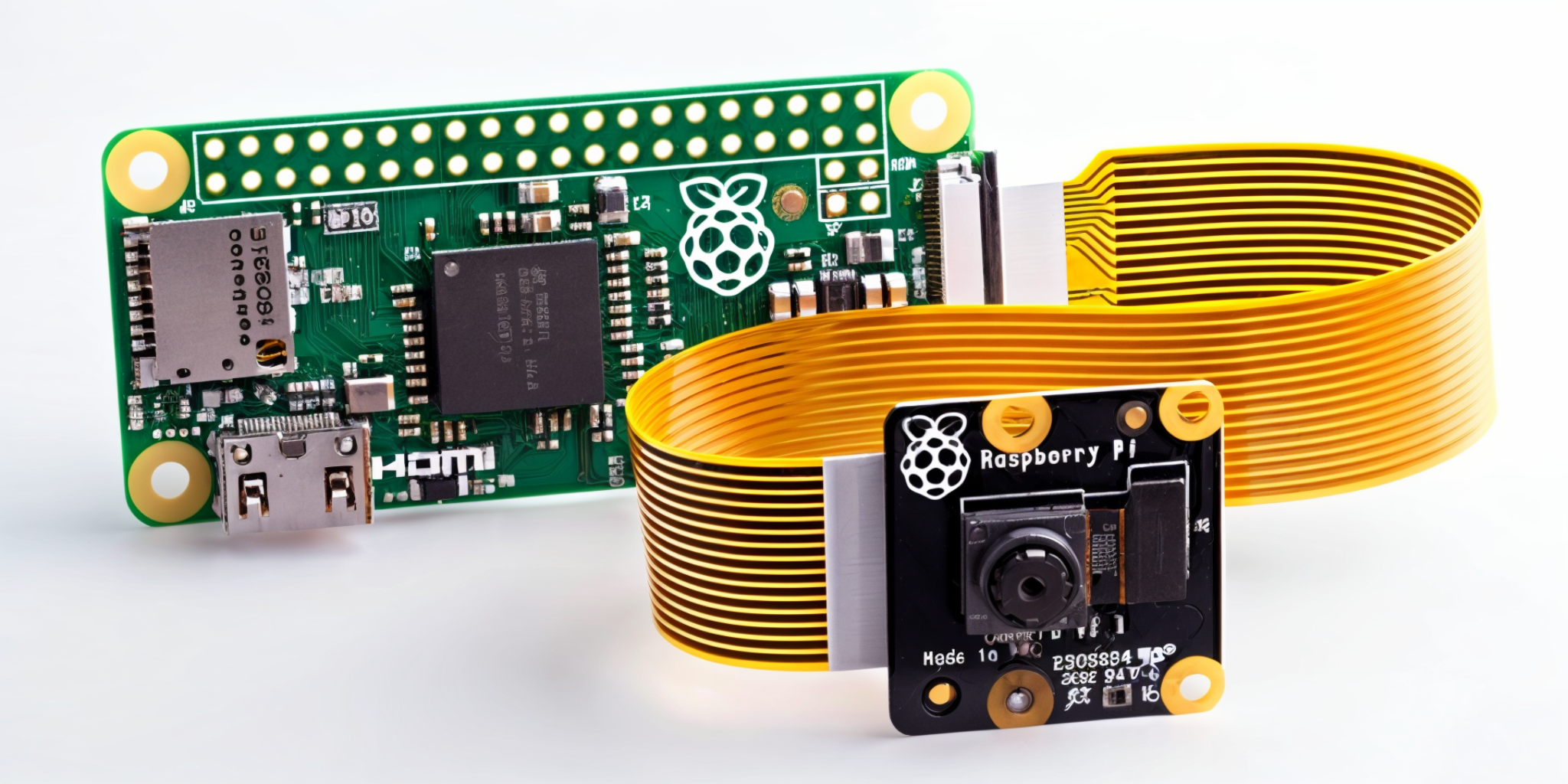

The biggest difference between embedded vision and what is often referred to as a machine vision system is that embedded vision systems are all-in-one devices, i.e., embedded vision is a collection of embedded systems and machine vision technology.
The difference between embedded vision and traditional machine vision
The traditional machine vision system consists of three parts: camera system, image processing system and output display system. The camera is connected to the PC through a network port or USB interface; the camera collects image information and transmits it to the computer for image recognition processing.
And the embedded vision system hardware integrates the camera module and processing board, combining image capture and image processing functions in one device. The device supports edge computing, receiving and processing data, making decisions, and then sending the data to other devices, or local or cloud-based processing and analysis. The compact design can be easily embedded in industrial and mobile devices, with low power consumption, reduced broadband requirements, and lower latency.
Embedded vision system architectures are diverse, with a range of custom and standard components。
The Typical components in an embedded vision system are:
- Embedded processor - Performs algorithms and controls device
- Camera module - Captures images/videos from scene
- Lens - Adjusts FOV to application needs
- Memory - Stores images, program code and data
- Interfaces - Connect camera, memory and I/O devices
The Advantages of embedded vision
Embedded vision is characterized by its small size, real-time nature and deployability at edge locations. It allows intelligent vision functions to be built into the device without the need for external processing hardware.
Embedded vision system is easy to use, easy to maintain, easy to install, etc. It can quickly build a reliable and effective machine vision system, thus greatly accelerating the development speed of the application system.
Compared to traditional machine vision, embedded vision systems are less costly. Even high-end customized embedded vision systems are cheaper than machine vision systems. The main reason for this is because embedded vision systems have low hardware requirements, which makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications, even with high integration costs.
In addition to this, embedded vision systems are characterized by ease of use, ease of maintenance, ease of installation, low energy consumption and streamlined design. The ability to quickly build a reliable and effective machine vision system, which greatly accelerates the development of applications, is ideal for tight spaces and integration with existing systems. But the real advantage of embedded vision is that its components do not negatively impact existing systems.
Embedded vision systems can do things that traditional machine vision systems cannot. Embedded vision systems can capture and process images, enabling mechanical systems to react to the world around them and enhance their autonomy. Embedded vision systems can react to and recognize images through deep learning, enabling mechanical systems to make decisions based on the surrounding environment.
The challenges embedded vision will face
Embedded vision faces several challenges, which are mainly related to technical implementation, resource constraints, and characteristics of the application domain. The following are some of the major challenges:
1. Processing speed: Embedded vision systems need to process a large amount of visual data in real time, which requires high-speed processors and efficient algorithms to support in order to ensure real-time performance and accuracy.
2. Power Consumption Problem: Since embedded vision systems consume a lot of computing and processing power, this is a major challenge for small devices (e.g., smartphones, drones, etc.) that rely on battery power. How to reduce power consumption while ensuring performance is a key issue that needs to be addressed in embedded vision technology.
3. Memory and storage constraints: Embedded vision systems need to process large amounts of vision data, which requires a large amount of memory and storage space to support. However, memory and storage resources are limited in many embedded devices, which limits the application scope and performance of embedded vision systems.
4. Limited embedded resources: In addition to the memory and storage limitations mentioned above, embedded systems also have limited resources such as arithmetic power and bandwidth. How to achieve efficient visual processing with limited resources is a challenge that embedded vision technology needs to face.
5. Optimisation of algorithms and models: Embedded vision systems require complex computer vision algorithms and models. These algorithms and models need to be optimised for the characteristics of embedded systems in order to reduce the amount of computation, lower power consumption, and adapt to the needs of real-time processing.
6. Security and privacy: As embedded vision technology is more and more widely used in various fields, how to ensure the security and privacy of data has become an important challenge. Effective encryption and privacy protection mechanisms need to be designed to prevent data leakage and misuse.
Applications of Embedded Vision Systems
Embedded vision system can achieve image recognition, image detection, image tracking, visual positioning, object measurement, object sorting and other applications. It is widely used in industrial manufacturing, electronic semiconductor production, logistics, robotics, automotive autopilot, drones, consumer electronics, security monitoring, medical diagnostics and other fields.
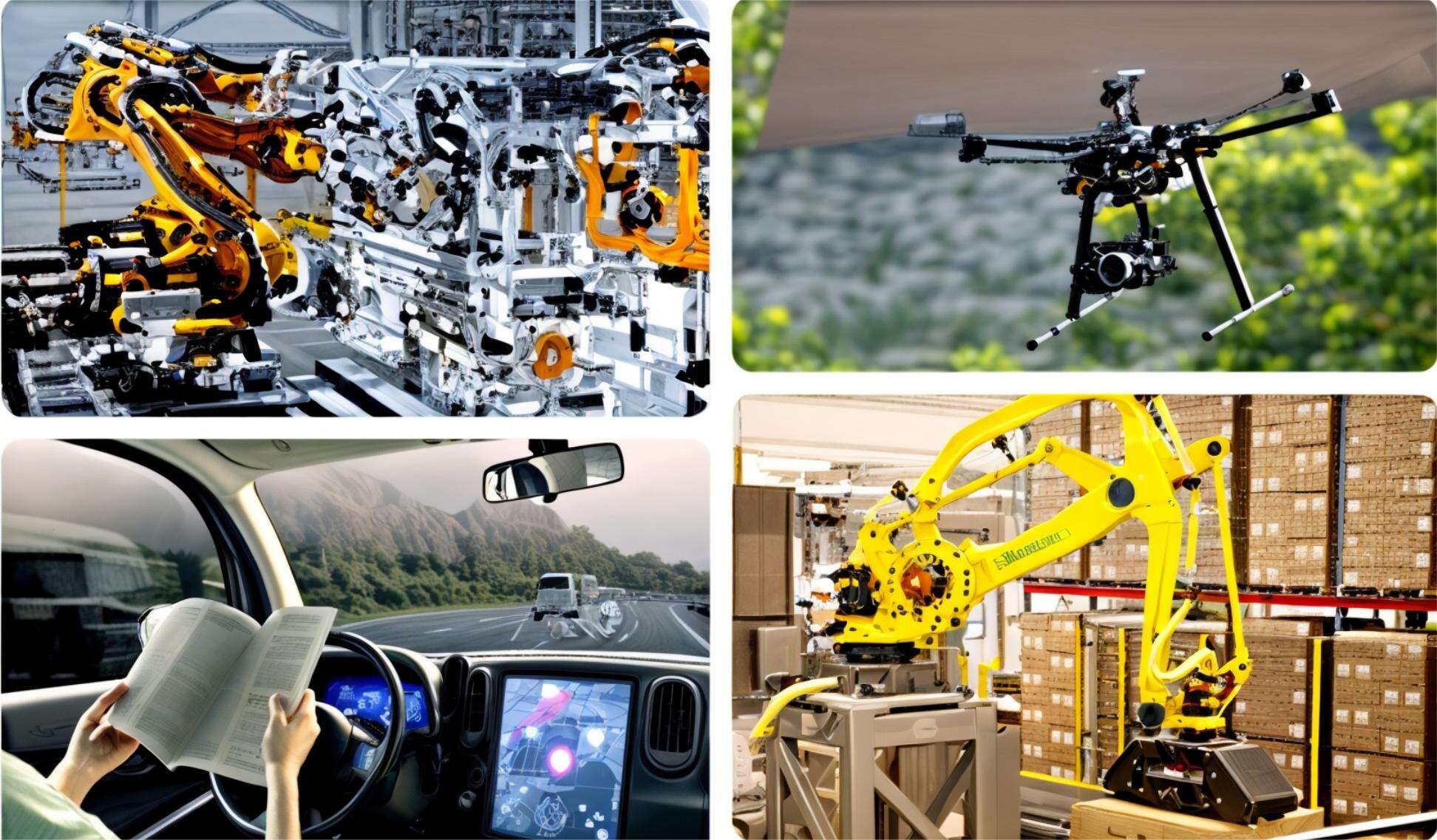
Conclusion
Along with the development of Industry 4.0, the demand for vision systems in the industrial market will grow, and more and more industries are deploying embedded vision solutions. The advantages of embedded vision systems over traditional machine vision systems are more obvious; they are typically cheaper, consume less power and have a more streamlined design. In most cases, embedded vision technology can meet application requirements that machine vision systems cannot.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD














