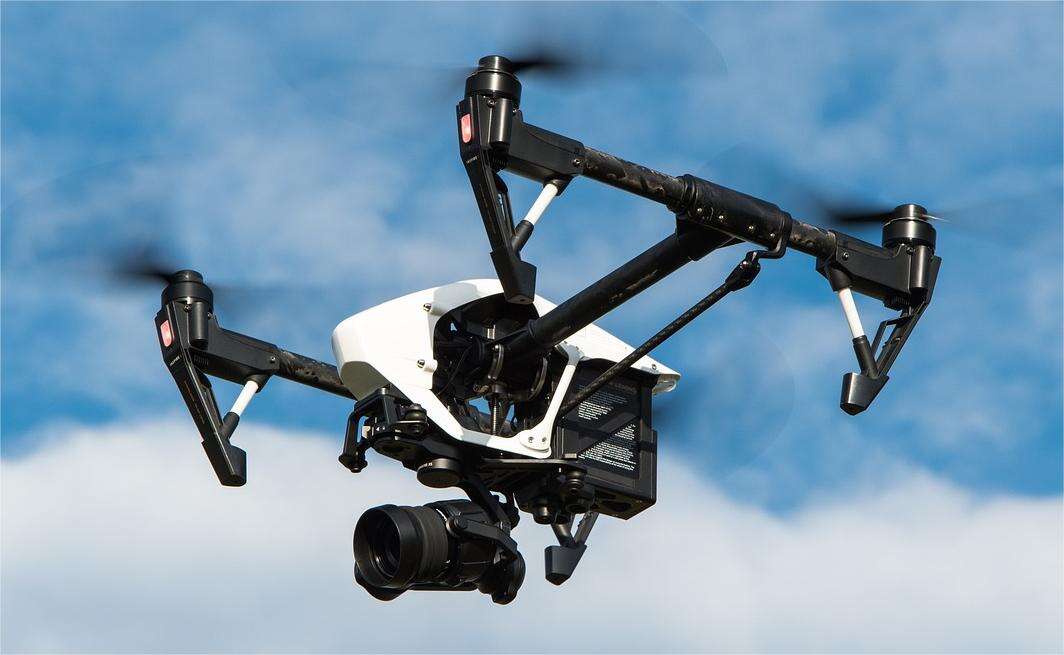
Drone-Based Scanning: Revolutionizing Data Collection and Mapping
The technology of drones with camera modules giving a new methodology to numerous sectors in the past few years including data acquisition and mapping. Drone scanning also known as the aerial photogrammetry enable the usage of cameras for capturing high definition images or creating a three dimensional map of the terrains or structures or objects at much lower costs. Here in this guide, an understanding of the features, the advantages and how drone scanning is revolutionizing the acquisition and analysis of spatial data will be made.
What is Drone-Based Scanning?
Drone-based scanning can be explained as using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or, as they are more popularly known, drones fitted with high-resolution camers and other sensing instruments to capture images of the Earth’s surface. It is done to reconstruct the images and come up with models, orthomosaics, and point clouds which are very standardized. The data resulting from the applications of the methods can be utilized in several applications, such as land surveying, infrastructure inspection, environment monitoring, and urban planning.
This advanced scanning capability relies on the integration of a variety of cutting-edge technologies, such as:
High-resolution cameras: Drones can be equipped with state-of-the-art camera modules to capture detailed aerial imagery, including high-resolution still photos and video footage.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR): LiDAR sensors mounted on drones can generate highly accurate 3D point cloud data to create detailed terrain maps and 3D models.
Multispectral and Hyperspectral Sensors: Drones can carry specialized sensors that capture data at multiple wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum to detect and analyze specific materials, vegetation, or environmental conditions.
Thermal Imaging: Infrared cameras on drones can provide valuable information about thermal characteristics, infrastructure conditions and other temperature-related data.
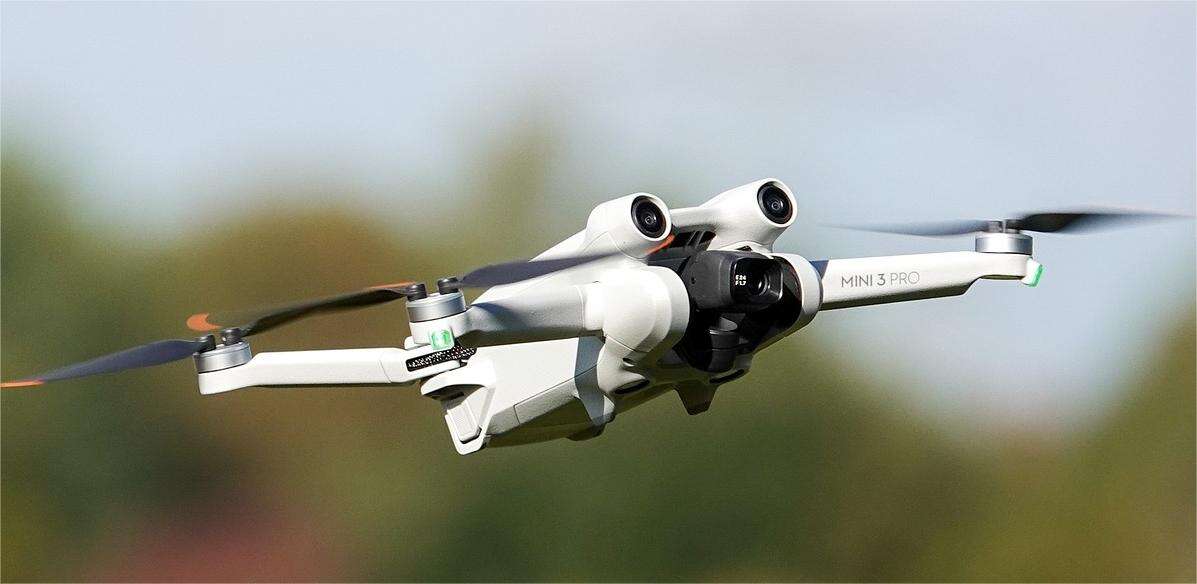

Advantages of Drone-Based Scanning
Cost and Time Efficiency
The data collected from drone-based scanning is cheaper and relatively faster than other manual methods of data collection. Earlier, capturing aerial image meant having to hire manned aircraft or satellite imagery which are time-consuming and costly to organize. Using drones, different data can be gathered fast and effectively which enable the gathering of data more frequently and therefore updated. This efficiency turns into short project duration and therefore less expenses.
High-Quality and Accurate Data
Modern unmanned aerial vehicles come with camera equipment that offers high resolution; thus, they provide accurate imagery. The images can be compiled to provide orthomosaics, which are orth ℝ directed aerial images of the Earth that are georeferenced. Moreover, drones are capable of collecting data from different angles at a time, which increases the reliability of making 3D models and point clouds. Such detail also assists in decision-making or analysis in numerous industries since the higher the level of details the correct the result.
Safety and Accessibility
For instance, using drones for scanning reduces the need of having people go to risky and or difficult terrains. However, another area that drones have proven useful is in sensing and data collection especially in areas that are inaccessible or there is a risk to human life. This accessibility creates many more opportunities in such areas as evaluation of constructions, monitoring of catastrophes, and studying of the environment. They can cover territories which are difficult to access or take a lot of time, effort and resources to access.
Applications of Drone-Based Scanning
Land Surveying and Mapping
Aerial scanning using drones has taken a new dimension in the field of surveying and mapping of the land. The traditional ways of surveying are sometimes done by direct measurements and involve much time in the field. Largescale areas can therefore be covered in relatively shorter times compared to if it were on the ground and the acquired data can be used to produce topographic maps, DTMs and contour lines. This data is very crucial in the planning and development of the urban structure for new constructions and the management of land resources.
Infrastructure Inspection and Maintenance
It is a critical task to inspect infrastructures like bridge, buildings, power lines, and other such securities, but it consumes time and requires resources. Bar codes consisting of high density and thermal imageries allow for fast and efficient appraisal of structures, as well as the discovery of problems with the structures such as cracks, corrosion, and heat abnormalities. These practices mean that infrastructure inspection can be done responsibly and before it becomes a plan to fail or anything near to that.
Precision Agriculture
Drone based scanning can be very much useful for the farmers to optimize the crop yield, to monitor the health of the plant and to detect them at the initial stage.
Multispectral sensors enable quantification of slight variations in condition of plants and their nutrient needs so to apply the resources in the right places and amount.
Considerations and Challenges
While the benefits of drone-based scanning are numerous, it's essential to consider the following factors and potential challenges:
Regulatory Compliance:
The operation of this aerial systems for commercial and industrial purposes is regulated by various measures and directives which must be complied to in order to avoid compromising of these systems and operations.
Data Security and Privacy:
Since the application involves the collection and storing of high-resolution images as well as 3D models, it is important to ensure there are adequate security protocols and standards fow the data, not forgetting the international regulations on user’s privacy.
Ongoing Training and Maintenance:
Practical implementation of scanning systems, based upon the drone technology involves training of operators and regular checks of the equipment’s performance to reduce on operational hitches and equipment failure.
How to perform better drone scanning missions
To maximize the effectiveness of drone-based scanning, consider the following tips:
Plan and Prepare: It is also important to plan for your flight path and goals before you start your flying with the drone. Depending on the circumstances, one can consider the effect of weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and the peculiarities of the task at hand. Make sure your equipment, batteries, and memory card are ready before the operation you are planning for.
Calibrate and Test: Make preliminary settings on the drone and the sensors before flying your drone to avoid capturing inaccurate data. Fly test to confirm the operation of the equipment, and fix the problems that may be there. These guidelines should be followed to ensure that the given data is of high quality and is accurate; Frequent maintenance and calibration will assist in the achievement of this goal.
Capture Overlap: It is very important that when capturing the imagery you should ensure that there is enough overlap between the successional images. This overlap is critical because it helps in proper stitching, building of orthomosaics, construction of 3D models. Ideally, the forward and side calibrated overlaps should be at 70% or higher.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What type of camera should I use for drone-based scanning?
A1: It all depends on your use-case and how much detail you wish to capture and in what way. Use cameras with a large sensor size and high megapixel count for high-resolution imagery. Certain drones have modularity to affix specialized sensors like thermal camera or multispectral camera for unique use cases.
Q2:How accurate are the 3D models and measurements generated from drone-based scanning?
A3: How as well as how accurate a 3D model is as well as the measurements depends on a number of factors among which is the quality of the images from the camera, the accuracy of the GPS onboard the drone as well as the processing software used. Broadly, drone-based scanning can deliver sub-centimeter accuracy, which is good for anything from land surveying to infrastructure inspection.
Q3: Can drones be used for mapping large areas?
A3: Yes.Indeed, drones are able to map large areas in a very efficient manner through the use of autonomous flight planning software. This allows you to outline what area you want covered and automatically creates flight lines which can cover it entirely. Due to drone technology, mapping large tracts of land has become speedier and more economical as opposed to past methods.
Conclusion
Drone scanning is an innovative technology that changes our perception of the way data is collected, analyzed and used in various fields. Drone scanning enables to carry out surveys, monitor environment and inspect infrastructure using high-resolution aerial imagery, 3D mapping and specialized sensors. Moreover, as this technology evolves and becomes more affordable, drone-based scanning will find new areas of application, eventually enabling us to manage resources efficiently and make decisions based on reliable data only.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD