How do embedded vision cameras play a role in post-operative and home patient care?
In the rapidly evolving healthcare sector, entities from medical service providers to equipment manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies, and health insurers are continuously innovating to meet patient needs. The healthcare system operates across four levels: patients, caregivers, organizations like hospitals and clinics, and the economic sphere, including regulatory bodies and pharmacy benefit managers. In the era influenced by the pandemic, ensuring quality post-operative and home care has become a global patient demand.
Hence, there's a growing need for an alternative method to measure vital signs without physical contact. Embedded vision technology has made groundbreaking progress, assessing patients' health conditions remotely using cameras, eliminating the need for patients to visit hospitals or clinics. This technology's advancement has enabled seamless communication between patients and caregivers, enhancing both inpatient and home care experiences.
Historical evolution of patient care
The evolution of patient care has seen a shift from traditional models relying on face-to-face diagnosis and treatment to a more patient-centric model. Post-operative care now extends beyond hospital treatment to continuous monitoring and support after discharge.
With the advancement of wearable technology, Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has become a reality. These devices, equipped with advanced sensors, monitor key vital signs like ECG, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, blood glucose levels, and body temperature. Real-time monitoring of this data provides invaluable information for medical professionals, aiding in accurate diagnoses and timely treatment decisions.
However, these wearable devices have limitations. They require direct contact with the patient, risking infection or discomfort from prolonged use. Additionally, battery life and data accuracy can be issues.
The medical industry is thus seeking solutions to monitor vital signs without direct patient contact. This is where embedded vision technology steps in. By integrating high-resolution cameras into medical devices, medical professionals can remotely assess patients' health without requiring them to visit hospitals or clinics. This development has not only improved the quality of patient care but also provided greater convenience and comfort for patients.
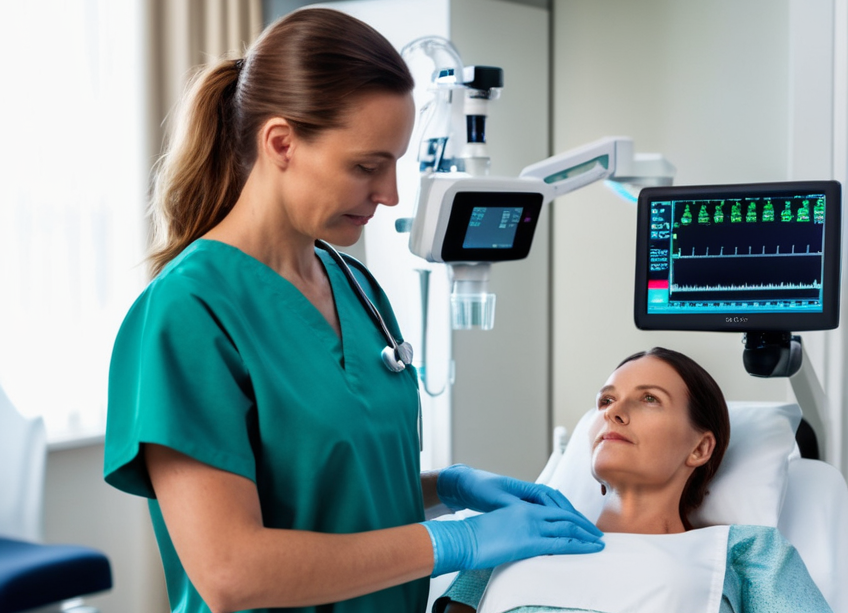

How do embedded vision systems impact patient care?
Embedded vision systems capture physiological parameters like skin color, breathing patterns, and heart rate using high-resolution cameras. This data can be used for real-time health monitoring and analysis. Moreover, these systems can assess pain levels and emotional states by analyzing facial expressions and body movements, providing caregivers with comprehensive patient information.
The application of embedded vision technology is particularly notable in post-operative and home care. For instance, monitoring patients' recovery progress via cameras allows medical staff to track rehabilitation remotely and adjust treatment plans accordingly. The technology can also prevent falls and respond to emergencies by monitoring patients' activities and notifying caregivers immediately upon detecting abnormal behavior or potential fall risks.
Telehealth is another significant application area for embedded vision technology. With telehealth devices, patients can receive professional medical consultation and treatment at home without visiting hospitals. This remote interaction not only increases the accessibility of medical services but also alleviates the burden on hospitals and optimizes the distribution of medical resources.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further expanded the potential of embedded vision technology. AI algorithms can analyze data collected from cameras, automatically recognize abnormal patterns, predict potential health issues, and provide personalized care recommendations. This intelligent care model not only improves the efficiency and quality of care but also offers patients more personalized and precise medical services.
What are the key camera features of camera-based patient care systems?
To ensure the embedded vision system's maximum effectiveness in patient care, selecting cameras with appropriate features is crucial. Here are some key camera module characteristics essential for achieving high-quality remote patient monitoring and diagnosis.
- High resolution: Essential for clear patient views during remote diagnostics, fall detection, or motion tracking. High resolution also ensures image or video clarity when zooming in on specific areas. For instance, cameras offered by e-con Systems, with resolutions up to 18MP, meet strict medical imaging requirements.
- High dynamic range: Necessary for adapting to varying lighting conditions in patient care settings. HDR ensures reliable capture of both the brightest and darkest areas of a scene, crucial for accurate imaging at different times, such as nighttime.
- Optical or digital zoom: Allows doctors to zoom in on specific areas like eyes or skin for closer observation. Cameras should offer either optical or digital zoom capabilities, with high-resolution cameras recommended for digital zoom to achieve the best output.
- Pan and tilt: Cameras used in telehealth or patient monitoring devices must be able to rotate and tilt to capture a complete view of the patient or surroundings, vital for accurate diagnosis or analysis.
- Low light performance: Recommended for reliable imaging in limited lighting. Low light cameras, such as those based on Sony STARVIS sensors offered by e-con Systems, ensure proper imaging at light intensities as low as 0.1 lux.
- Near infrared performance(NIR): Essential if the device uses infrared lighting for night vision. Cameras must be sensitive to the near-infrared spectrum to produce high-quality images.
- Long cable support: Needed if the distance between the device and server exceeds three meters. Interfaces like Ethernet, GMSL, or FPD Link are recommended for long-distance transmission of image or video data.
- Edge AI processing capability: Required for AI-based patient care analyses like fall detection, vital sign measurement, and people counting in medical rooms. Cameras must provide images ready for processing by processors compatible with edge-based processing platforms.
- Easy configuration and maintenance: Cameras should be user-friendly, allowing adjustments to imaging parameters like sharpness, contrast, brightness, and saturation. Maintenance should also be straightforward for better usability and staff experience.
Specific applications of embedded vision in patient care include:
Telehealth
Enables medical professionals to examine patients remotely, facilitating analysis of vital signs when practitioners and patients are not co-located. High-resolution cameras provide clear, comprehensive patient views in crowded environments like NICUs, allowing rapid condition assessment. Telehealth devices also facilitate communication between patients and their loved ones within the hospital, especially during pandemics when isolation is required.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Contactless and continuous monitoring via camera imaging can detect falls promptly. Patient monitoring systems with cameras leverage computer vision for context monitoring of facial expressions, body movements, and activity recognition, providing advanced analysis. Combined with AI, embedded vision technology greatly enhances Remote Automated Monitoring (RAM) capabilities in post-operative and home care, offering a wide range of audio, video, digital, and processing and analysis functionalities.
Rehabilitation
Post-surgical patients benefit from rehabilitation programs that monitor movements to assess progress over time. Camera systems in rehabilitation are used for motion tracking, or kinematic measurement, requiring cameras to accurately capture movements of the patient's arms, legs, or other body parts, depending on the area under examination. The captured image data is input into a software system to derive parameters indicating the patient's condition.
With the development of artificial intelligence algorithms, it can automatically diagnose certain diseases to a certain extent, which is a big step that cannot be ignored for post-operative and home care. The embedded vision camera can provide the most detailed image data protection.
If you are developing a camera-based medical care device, choosing the right camera module for integration is an important decision. Sinoseen, as a Chinese camera module manufacturer with more than 14 years of industry experience, provides feasible embedded vision solutions for many industries. If you encounter related problems in camera-based medical device engineering, please feel free to contact us. Sinoseen will provide you with the most professional vision solutions.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD