Near-infrared cameras: What is it? How does it work?
NIR imaging is a cutting-edge technology offering unique perspectives in the wavelength range of 650nm to 950nm. Unlike visible light imaging, NIR is less affected by color changes, enabling high-precision visualization of any object. This distinctive feature makes NIR imaging a forefront technology in numerous fields, from medical diagnostics to industrial quality control.
What is NIR imaging technology?
NIR imaging technology marks a significant advancement in the field of optical imaging. It utilizes the electromagnetic spectrum, specifically wavelengths beyond the visible light spectrum, ranging from 650nm to 950nm. Capable of penetrating complex objects, it provides detailed images under various conditions.
NIR imaging employs continuous wave motion principles, offering a unique sensitivity curve that clearly projects distant objects. Compared to traditional imaging methods, NIR imaging is not color-dependent, meaning it can provide high-contrast images, making them easier for human observers to interpret.
One of the main advantages of NIR imaging is its ability to penetrate certain materials, such as plastics and human tissue. Additionally, NIR imaging systems can operate effectively under low-light conditions, with good sensitivity and high-resolution capabilities.
However, NIR imaging also faces some challenges. For instance, objects with wavelengths beyond 700nm to 1000nm may not be visible to NIR camera module. Moreover, due to the lack of ambient light, NIR imaging may require additional light sources in nocturnal scenarios.
How is NIR imaging achieved?
The realization of NIR imaging demonstrates the progress in sensor technology and understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. NIR imaging is achieved through specialized cameras sensitive to the near-infrared range near the visible spectrum. It covers wavelengths just beyond the range of visible red light, which is approximately 700nm, up to 950nm.
NIR cameras, such as those used for night vision or traffic monitoring, are designed with sensors highly sensitive to the near-infrared spectrum. Traditionally, CCD sensors were used for NIR imaging, but the emergence of CMOS technology has revolutionized the field. CMOS sensors exhibit greater sensitivity in the near-infrared range, especially above 850nm, making them more cost-effective and suitable for a broader range of applications.
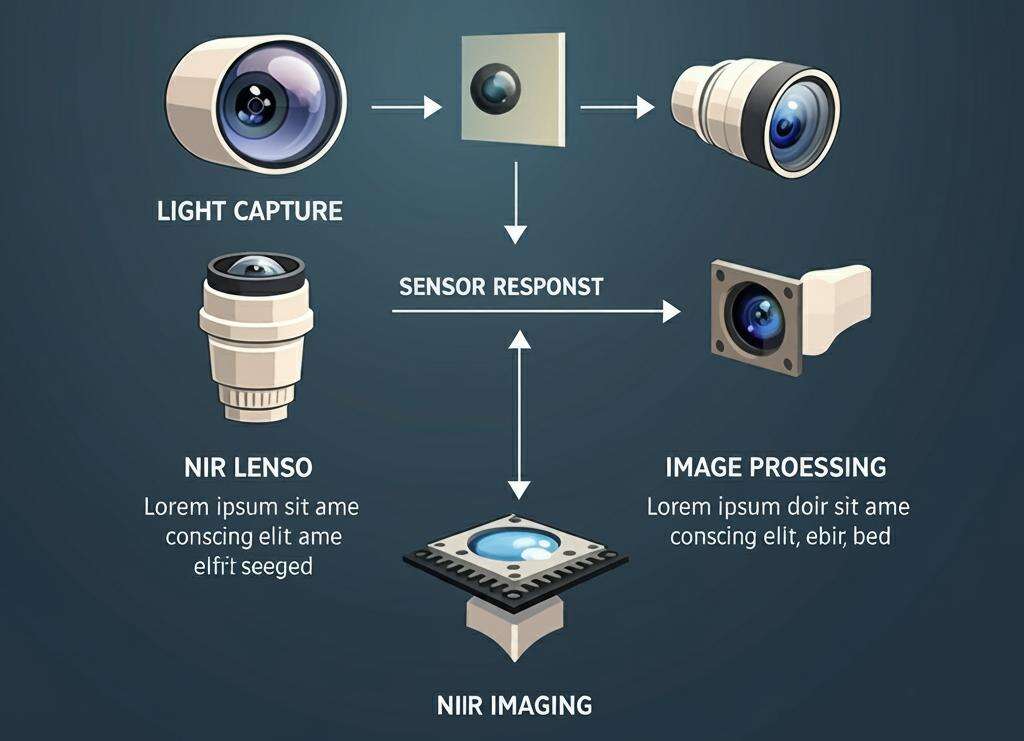
To achieve NIR imaging, cameras are typically equipped with a thicker base layer, which is more sensitive to the near-infrared spectrum than the visible spectrum. This allows for the capture of high-quality images even in extremely low ambient light. The process involves the following steps:
- Light capture: NIR cameras are fitted with lenses that focus near-infrared light onto the camera's sensor.
- Sensor response: The sensor within the camera converts the captured light into electrical signals.
- Image processing: The electrical signals are then processed to create a digital image that can be analyzed or displayed.
Moreover, the quality of NIR imaging can be significantly enhanced using specific techniques and tricks. For instance, image intensifiers can boost the camera's ability to capture usable images under low-light conditions. Additionally, the use of filters can help block unwanted wavelengths, ensuring that the camera only detects near-infrared light relevant to the current application.
Growing demand for NIR imaging
According to recent market research, the NIR imaging market is on an upward trend. The market size has doubled from approximately $285 million in 2019 and is projected to reach $485 million by 2030. This growth can be attributed to the increasing adoption of NIR technology in healthcare, security, agriculture, and industrial inspection.
How do NIR cameras work?
NIR cameras are designed to detect and process light within the near-infrared range, typically between 700nm and 1000nm. This is achieved through specialized sensors that are more sensitive to infrared light than visible light. The high quantum efficiency (QE) of these sensors ensures that a majority of incident photons are converted into electrons, which are then processed into usable images. Quantum efficiency is a key parameter for NIR camera performance. It measures the camera's ability to convert incident photons into detectable electrical signals. A higher QE means better image quality, even under low-light conditions.
Once NIR light is captured by the camera's sensor, it undergoes a series of image processing steps. These steps may include noise reduction, contrast enhancement, and color correction. Advanced image processing algorithms can also be used to extract specific information or enhance the visibility of certain features in the image.
NIR cameras typically use color filters to improve the quality of the captured images. For example, RGB color filters can be used to simplify palette selection and improve color accuracy. However, in NIR imaging, these filters can be adjusted or replaced with infrared-pass filters to allow more near-infrared light to reach the sensor, resulting in clearer images.
Proper exposure control is crucial for capturing high-quality NIR images. Overexposure can cause image washing out, while underexposure can lead to noisy or dark images. NIR cameras usually have automatic exposure features that adjust exposure time and aperture to achieve the best image under varying lighting conditions. Additionally, maintaining the correct aspect ratio ensures image distortion is minimized, which is vital for accurate analysis and interpretation.
Capturing images in RAW format provides greater flexibility in post-processing as it preserves more of the original image data. This is particularly useful in NIR imaging, where analysis often requires the highest possible image quality. Using high-quality IR filters can also enhance image clarity by blocking unwanted light wavelengths.
Common applications for NIR cameras
Research and Development (R&D)
In the R&D sector, NIR cameras are invaluable for analyzing materials with unique NIR spectral characteristics. They assist scientists and researchers in identifying and quantifying specific substances, which is crucial for drug development, chemical analysis, and materials science.
Biometrics and Access Control
NIR technology plays a significant role in biometric systems, particularly iris recognition. The technology can capture detailed images under various lighting conditions, making it an ideal choice for secure access control applications.
Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, NIR cameras are used for quality control, inspecting products for defects or foreign objects, and monitoring manufacturing processes. They can also be employed in agriculture to assess the health of crops and predict yields.

Sinoseen: Your Partner for NIR Imaging
Sinoseen boasts over 14 years of experience and expertise in the field of embedded vision, with a professional team that has provided dedicated NIR camera support for more than 50+ clients. Should you require the integration of a suitable camera for NIR imaging, feel free to contact us, and we will offer you the most professional one-stop customized service.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD














