Motion JPEG vs H.264: Understanding the Difference in Video Compression Codecs
With regard to video compression, mjpeg(Motion JPEG) vs h264 are among the most commonly used formats, but mjpeg(Motion JPEG) vs h264 have obvious differences.
what is Motion JPEG (M-JPEG)?
mjpeg applies JPEG compression individually to each video frame. This provides high image quality since each frame is uncompressed relative to other frames. However, mjpeg files are very large as it doesn't exploit inter-frame correlation.
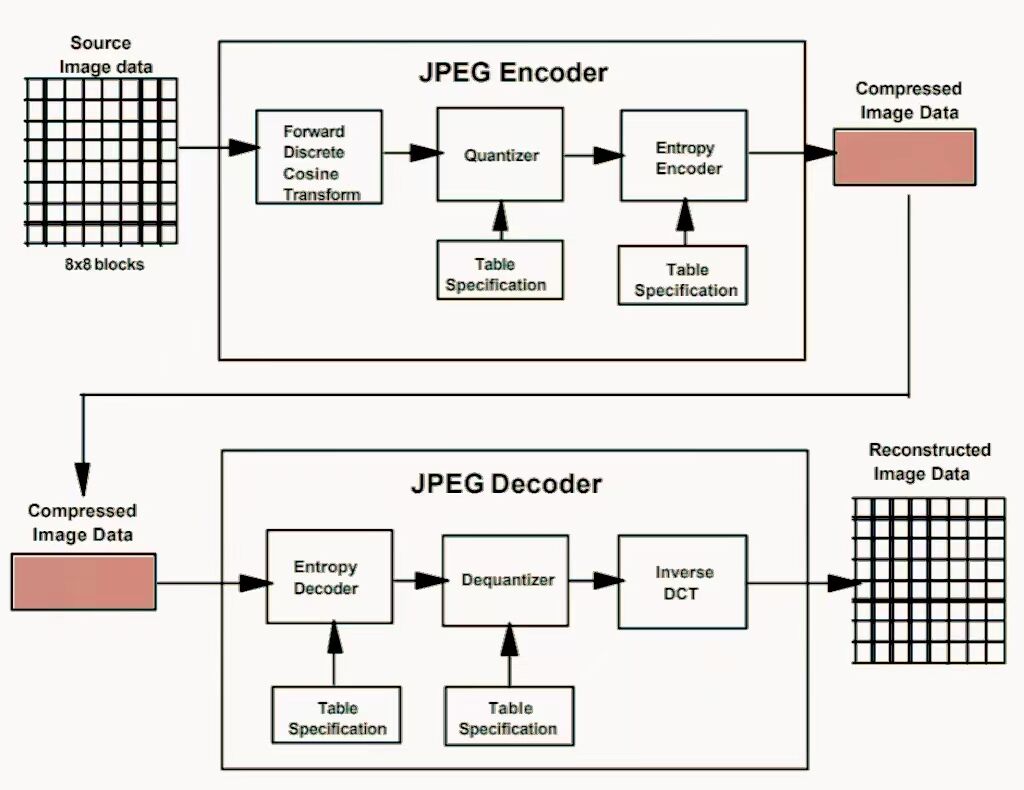
Here are some key features of Motion JPEG:
Image Quality: By compressing frame by frame, m jpeg gives the most excellent image quality as a result. Hence, in this regard, it enables to use it as a replacement for high-band width connection when the details of the mjpg video have to be preserved, e.g. medical imaging and video editing.
Simplicity: M-JPEG is a simple codec which is advantageous when the implementation and decoding is difficult. The codec uses significantly less computational power to produce the encoded and decoded versions as compared to the latest available compression codec.
Random Access: So, each frame can be individually compressed that leads to possible (random) access at any point of the video sequence m jpeg. Also in mass-cognition case it provides fast processing but is not appropriate for variance extraction and slow motion.
File Size: Just that, the decompressible file size of M-jpeg is also higher and occupies more space than other codecs. In such a case, each given frame is compressed by itself independently. Consequently, it is without any inter-frame compression that leads to bigger file sizes and result in high storage requirements.
Bandwidth: Being larger in file size, m-jpeg codecs would require more bandwidth to convey in comparison to others. Such a feature can feel inconvenient in cases of low network bandwidth or video streaming being over the internet.
what is H.264?
h.264h , also called MPEG-4 AVC, uses inter-frame encoding which analyzes both spatial and temporal redundancies across frames. It breaks frames into macroblocks and applies predictive coding techniques to remove redundant data. As a result, H.264 provides significantly higher compression for the same quality level as m jpeg with file sizes up to 80% smaller.
Here are some key features of H.264:
Compression Efficiency: h.264h is able to reach greater compression efficiency by taking advantage of the temporal associations between frames rather than the individual frames as it has been previously the case. It deploys functionalities like motion estimation and motion compensation to caucus the discrepancy between frames, leading to smaller file sizes.
Bandwidth and Storage: Because of its high compression efficiency, H.264 use less bandwidth and storage space for transmitting video than m jpeg . This therefore makes it fitting for purposes whose goal underpinning is to save bandwidth or storage space, such as video streaming and video surveillance.
Latency: h.264h protocols introduce some encoding and decoding latency because of its frame intercompression feature. This could be an issue for video transmissions with low latency (for live video conferencing, for example, or broadcasting services).
Complexity: H.264 requires a significant number of computational units for encoding and decoding operations. Thus, it is perceived as more intricate compared to m jpeg codec. Nevertheless, hardware acceleration and dedicated hardware for encoding and decoding phases, make the complexity of this process more bearable.
Compatibility: h.264h has a widespread of different platforms, devices and software options, making it a good choice for an encoding and decoding algorithm. It is also compatible with a variety of gadgets including smart phones, tablets, and the media players.
The main difference between mjpeg vs h264 :
- M-JPEG does not support parameter adjustments at bitrates channel varying while h.264h does.
- H.264 is thinner overall because of the more complicated functions involved in encoding/decoding compared with M-JPEG.
- M-JPEG is free of patents/licensing costs which is purely a fact for h.264h .
|
Description |
H.264 |
MJPEG |
|
Compression Technique |
Predictive coding, inter-frame compression |
Intra-frame compression |
|
File Sizes |
Smaller file sizes |
Larger file sizes |
|
Applications |
Video streaming, Blu-ray discs, and HD video conferencing. |
Video editing, Surveillance systems, medical imaging. |
|
Performance |
High |
Low |
|
Usage |
Widely used for all devices. |
Used but less |
|
Network Bandwidth |
Usage Less bandwidth |
More bandwidth |
|
Popular |
More |
Less |
How to Choosing the Right Codec?
If you have to choose between h 264 motion jpeg , then you should pay attention to what exactly your application needs. If image quality and random access are top priorities, whereas storage space or bandwidth are not a criterion, mjpeg may be a suitable pick. Conversely, those who emphasize efficiency, compression, reduced size of files, and compatibility across devices give priority to H.264.
It's worth mentioning that there are other video codecs available some of them are h265 (HEVC) and VP9 they are more efficient in compression than H.264. These newer codecs may be taken into account if you need more compression ratios or you are restricted by the compatibility requirements.
finally, with that knowledge about the contrast between h 264 motion jpeg , choosing the correct video compression codec for your application will be made much easier. Think about the image quality, file size, bandwidth, latency, and similarity when making your decision that is compatible with your demands.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD














